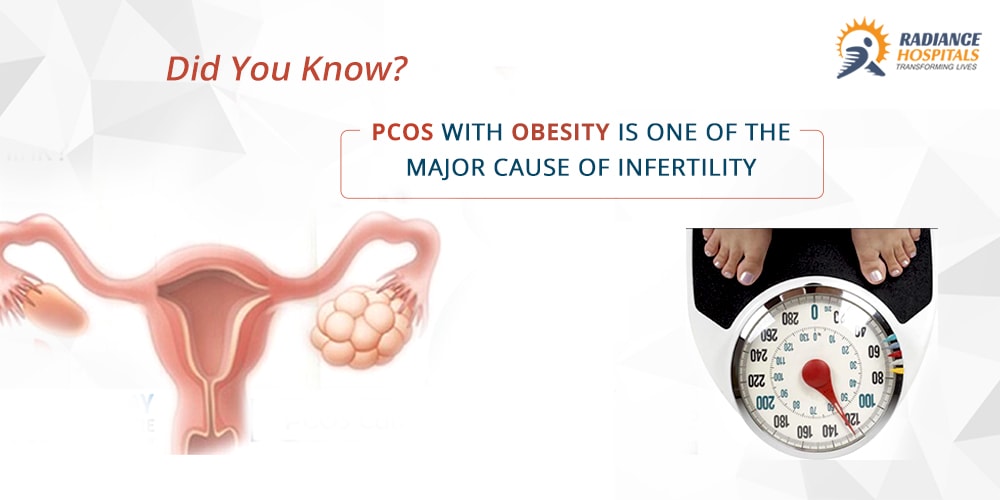
Infertility has become a bane of modern living and PCOS is one of the major causes of infertility.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome commonly called PCOS condition is a very common endocrine condition in reproductive-aged women often leading to difficulty in conceiving. Women diagnosed with PCOS can experience irregular periods, abnormal hair growth, acne, and can have ovaries containing multiple small cysts.
PCOS has a negative effect on fertility since such women are not able to ovulate or release an egg, each month due to an overproduction of estrogen. This subsequently leads to irregular periods and increased levels of hormones such as testosterone that can affect oocyte quality, inhibit ovulation, lead to insulin resistance, and increase the risk disorders such as gestational diabetes.
The relation between PCOS and obesity can be termed as complicated. Signs and symptoms of PCOS begin for some females soon after they start having periods. Women with PCOS produce too much insulin, or the insulin they produce does not function normally which leads to weight gain. Women diagnosed with PCOS may also find it difficult to lose weight. For some others substantial weight gain is followed by PCOS. However, it is certain that women suffering from obesity have a greater risk for PCOS and women with PCOS have a greater risk for obesity.
Many PCOS women with obesity may also develop coronary artery disease and glucose abnormalities at a very young age. Bariatric surgery can be a significant procedure to fight against all these abnormalities and a solution for all such irregularities. According to a study, in the state of Gujarat itself 18% females and 14 % of Males are over-weight.
If the prevailing PCOS condition is due to obesity, the chances of cure are almost close to 100% particularly young females with such condition. There are few types of surgeries and procedures for such condition, but your surgeon will likely have a recommendation as to which will be most effective for PCOS. The proven methods are Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) and Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG).
The Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) generates weight loss solely through gastric restriction (reduced stomach volume). In LSG approximately 2/3rd of the stomach is stapled off roughly the size and shape of a Banana or Sleeve. This operation does not involve any ‘rerouting’ or reconnecting of the intestines. Hence it is technically as simpler operation than the gastric bypass.
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is one of the latest advancements in Medical Science. Endoscopic Bariatric Procedure does not require any hole or incision to put on any part of the body but a special Endoscopic instrument is inserted through an oral route to reach the stomach. Then the size of the stomach is reduced using stitches. On the same day after 4-6 hours of the procedure, a patient can go home. Moreover, as the procedure involves zero blood-loss, there is no need for blood transfusion and chances of infections are also almost nil.
Related Articles
A new technique in Bariatric Surgery – Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty