Blood pressure is required for blood to flow and carry oxygen to vital organs of the human body. But it is when; this Blood pressure gets too high results into Hypertension. This may harm the arteries and cause the heart to work harder. More of adult medical conditions, but nowadays youth falling prey to it.
Risk Factors that lead to developing hypertension in adolescents include
- Family history has been linked to a higher risk
- Racial predilection has been seen, the African-American population is at higher risk
- Increasing body mass index
- Low birth weight and intra-uterine growth retardation
- Increased sodium consumption
Diagnosis of Hypertension in teenager emphasizes on
- Going through Patient History: A thorough history is essential in guiding the evaluation and management of a hypertensive adolescent
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical examination could give hint about the underlying cause of hypertension in children and the presence of target organ damage.
- Blood Pressure Measurement: The American Academy of Pediatrics, the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology recommend regular blood pressure screening in children above the age of 3 years at routine health visits.
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring uses a device that can be worn for 24 hours. It takes multiple blood pressure readings and can help get a more accurate reading of overall blood pressure.
Management of Hypertension in Youth can be achieved by
- Therapeutic Lifestyle Modification: Enhances on dietary management, increased physical activity, stress reduction and avoidance of drug and tobacco use. Dietary management should include age appropriate, a salt-restricted diet with an emphasis on weight loss in overweight or obese children.
- Pharmacological Therapy: Children who are symptomatic, who have diabetes or end organ damage such as left ventricular hypertrophy should all be prescribed antihypertensive medication. In addition, children with persistent hypertension after 6–12 months of instituting a heart-healthy lifestyle should also be prescribed a medication to lower their BP.
- Antihypertensive medications: Combination of drugs recommended if BP control is not achieved with a single drug.
Reports show the reversal of target organ damage following the institution of antihypertensive therapy in children. Seeman et al reported a regression in Left Ventricular Hypertension in a small pediatric cohort treated with ramipril (Antihypertensive medication) monotherapy over a 6-month period.
Other forms of therapy
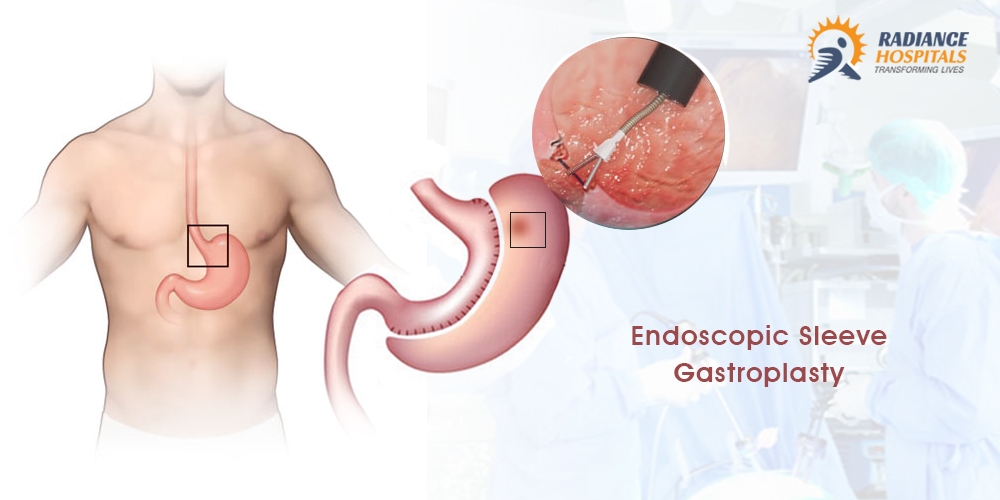
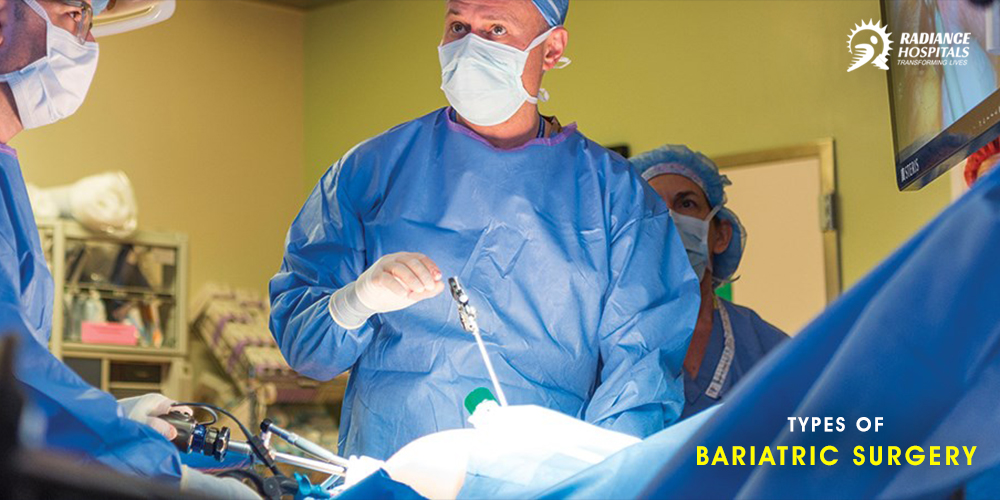
The emerging trend of utilizing bariatric surgery for reversing morbid obesity in adolescents is gaining awareness. Teen-LABS consortium published the largest series of prospectively collected data on 242 adolescent patients with a mean age of 17.1 (+/−1.6) and BMI of 53. Here in the patient’s Mean weight decreased by 28% with gastric bypass and 26% with sleeve gastrectomy, which was sustained at 3 years. Weight loss, the first line treatment with obesity-related hypertension leads to a decrease in Symptomatic hyperactivity, thereby lowering BP, providing experimental evidence for effective treatment of obesity-related hypertension.
Related Articles
Bariatric Surgery: The solution of Obesity surgery for Diabetes type 2